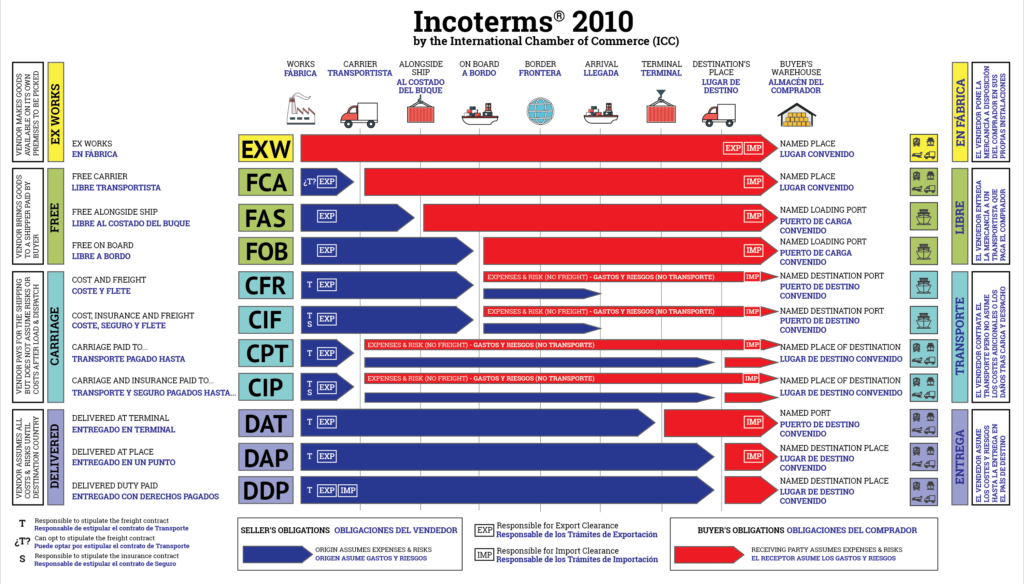
Concepts and terms of international sales:
One of the main issues in international sales is the separation of duties of buyers and sellers, which, because it is not necessarily governed by the laws of the importing and exporting countries, is governed by the rules of Incoterms according to international custom.
In this article, we try to explain more about how to buy that you can buy the product according to the terms: EXW, FAS, FCA, FOB, CFR, CIF, CPT, CIP, DAF, DES, DEQ, DDU, DDP Buy, Ebrahimi Trading Group introduces you to the purchase method that has the lowest cost and you can easily clear.

Delivery at the seller’s workplace:
EXW purchase term means that the importer receives the goods in the warehouse or factory and the cost of transportation to the port and loading and transportation and other responsibilities will be with the buyer. The price you get based on EXW is the minimum liability with the seller and the maximum liability with the buyer. Note that the seller does not even bear the cost of obtaining an export license or other licenses required to export the goods.
It is recommended to use this semester of purchase or payment term in road transport.
FAS: FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP Delivery of goods next to the ship on the dock (loading port specified at the origin)
The term is used in maritime transport and means that the seller places the goods at the designated port of shipment after the goods have been cleared through customs of origin and obtained an export license on the berth at the ship.
In the sense of FAS, the seller is obliged to clear the goods from the customs of origin and export license at his own expense and responsibility, and also the seller is responsible for paying all taxes, duties and taxes in FAS.
If you want to deal with this term, it is recommended that you agree in advance with the seller about the cost of the inspection.
FCA: FREE CARRIER DELIVERY TO CARRIER
The concept of FCA means that it is the seller’s responsibility to deliver the goods to the carrier at a designated place when the goods are cleared for export.
One of the duties of the seller is to obtain an export license and export license and to perform customs formalities and clearance of goods.
According to the experience of Ebrahimi Trading Group, the delivery of goods in the FCA term to the buyer or the transport company or any other person designated by the buyer is specified in one place, be sure to specify a place in your contract if the local contract does not provide He chooses the right place.
FOB: FREE ON BOARD Delivery until the goods pass through the ship’s railing
FOB is one of the most common trading concepts, meaning that the seller passes the goods through the ship’s railing at the designated port of call. FOB is used only for sea freight. In the FOB sense, the cost of loading the goods up to the deck and even under the deck is paid by the seller, but it is not his responsibility. Fall, the responsibility lies with the buyer.
Ebrahimi Trading Group suggests that if the arrangement of the goods is important to you, use the FOB STOWED term so that the seller is responsible for the arrangement cost.
CFR: COST AND FREIGHT Shipping costs and freight
CFR is exactly like FOB, only the shipping cost must be paid by the buyer at the origin.
In this type of CFR purchase term, if the goods are damaged, because the shipping company must be accountable to the seller and is not on the side of the buyer, he will shoulder the responsibility and according to the rules of Incoterms, his responsibility was to transport until crossing the fence.
The second point to note is that: CFR is divided into two categories: FREE OUT (the cost of unloading the goods at the destination is the responsibility of the buyer) and LINERFULL (the cost of unloading the goods at the port of destination is the responsibility of the seller).

CIF: COST INSURANCE AND FREIGHT Cost of goods, insurance, freight to the port of destination
In CIF, all duties are the same as CFR, with the difference that the seller must insure the goods by sea.
In CIF, the seller will consider the minimum insurance, so the suggestion is that if you have a specific insurance, you should mention it in the contract.
CPT: CARRIAGE PAID TO Shipping paid to a specific destination
CPT means that the seller pays the freight to the designated destination and the responsibility for the loss or damage to the goods is transferred from the seller to the buyer once the goods are under the carrier’s supervision.
Note that in CPT the seller is not responsible for loading the goods. According to experience, it is better to use the CPT method in land, air and combined transport (two modes of transport).
CIP: CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO Shipping and insurance fee paid to the designated place of destination
CIP is like CPT, except that the seller pays for the freight insurance to the destination.
Again, in CIP, the seller is not responsible for the loading of the goods, despite the fact that he pays the freight and insurance of the goods.
DAF: DELIVERED AT FRONTIER DELIVERY AT THE CUSTOMS BORDER
DAF means that the seller clears the goods for export and provides them to the buyer at the place specified in the contract before the customs border of the neighboring country. Mentioning the location of the border is very important because this term can be used for any border, including the border of the country of issue or even the border of the country of entry. DAF is mainly used for transportation by train and truck.
DES DUTY PAID: DELIVERED EX SHIP DELIVERY FROM SHIP
DES means that the seller places the goods at the port of destination on the ship carrying the goods before clearance for entry.
DEQ: DELIVERED EX QUAY Delivery at destination port and tolls paid with mention of destination port
In DEQ, the seller’s duty ends when the goods are delivered to the buyer at the port at the designated port of destination, after the goods have been cleared. The seller assumes all responsibilities and costs, including duties and taxes, commercial profits and customs duties at the destination.
Let the merchants know that DEQ is used under two headings: paid and unpaid tolls. Delivery at the port of destination and tolls paid means that the seller must obtain a permit to enter the goods in the destination country and arrange customs formalities at the destination in accordance with the regulations of the destination country and taxes and customs duties and remove the goods from customs and Give the green customs license to the buyer. However, in the case of DEQ, the seller pays the unpaid duties at the port of the destination country at customs, and the buyer is obliged to obtain an import permit from the destination country and pay customs formalities and customs fees.
DDU: DELIVERED DUTY UNPAID Delivery of goods to the buyer Unpaid tolls
DDU means that the seller delivers the goods to the destination and performs customs fees and formalities in addition to paying duties and taxes.
DDP: DELIVERED DUTIES PAID TO DELIVER the goods to the buyer, paid tolls
DDP means that the seller has a duty at the destination customs to pay the import duties to the country of destination and to collect duties and taxes and to accept the goods at the destination by performing customs formalities.
Incoterms DAF
Delivery of goods at the border:
The term delivery of goods at the border means that the seller delivers the goods when, after clearance for export and not for entry, on the vehicle bringing the goods, unloaded at the point and place specified at the border, but Before the customs border of the neighboring country – provide to the buyer. The term border may be used for any border, including the border of the exporting country. Therefore, it is important that the desired border is always determined by mentioning the name of the point and place in the term.
Of course, if the parties want the seller to take responsibility for unloading the goods from the vehicle that brought it and bear the risks and costs of unloading, he clarifies this by adding a clear phrase in the sales contract.
The term is used for a variety of modes of transportation and when the goods are delivered at the land border.
When delivering goods at the port of destination, on board the ship or on the dock, the terms delivery on board the ship at destination DES and delivery at the dock at the port of destination DEQ must be used.
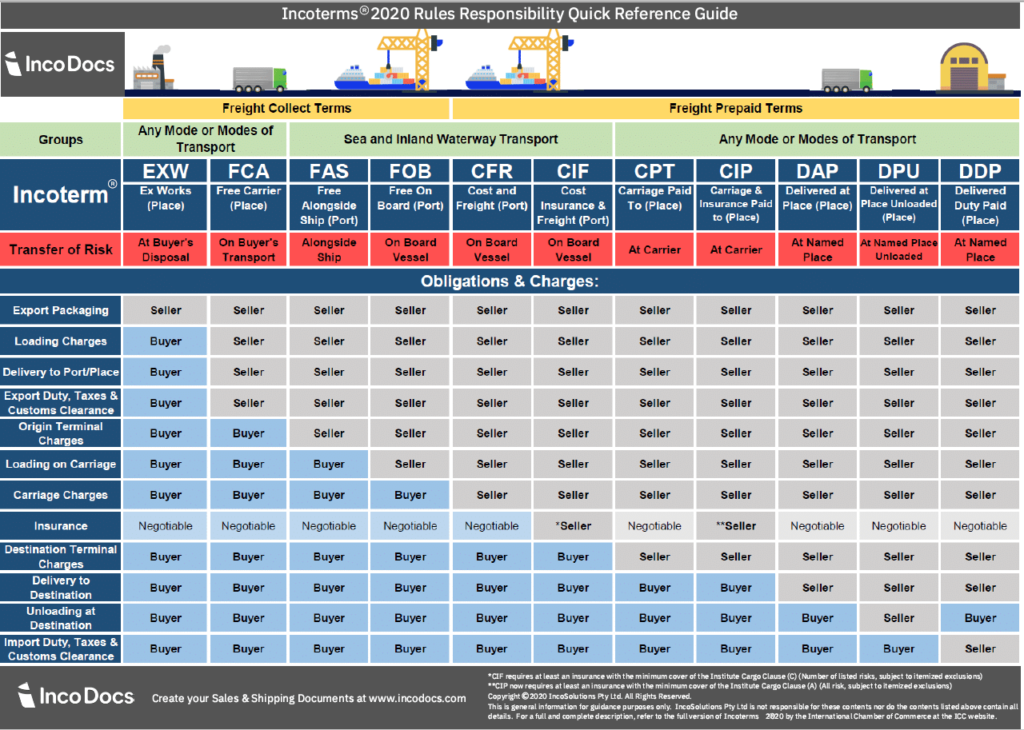
Delivery of goods to the place specified in the destination with clearance and payment of customs duties and taxes:
The term (delivery of goods at the place of destination with clearance and payment of customs duties and taxes) means that the seller of goods after clearance to enter, and if not unloaded from the vehicle of the goods, at the place of destination, Delivers the goods to the buyer.
The seller must assume all responsibilities for the goods and their costs, including customs duties and taxes, payment of formalities, taxes and other expenses related to the arrival of the goods in the destination country, if necessary.
The term DDP refers to the maximum liability of the seller.
If the parties wish to pay certain costs related to the importation of goods, such as VAT, the seller will be relieved of this responsibility, this must be clarified by adding a clear phrase to this end in the sales contract.
CIF: COST INSURANCE AND FREIGHT Cost of goods, insurance, freight to the port of destination
In CIF, all duties are the same as CFR, with the difference that the seller must insure the goods by sea.
In CIF, the seller will consider the minimum insurance, so the suggestion is that if you have a specific insurance, you should mention it in the contract.
CPT: CARRIAGE PAID TO Shipping paid to a specific destination
CPT means that the seller pays the freight to the designated destination and the responsibility for the loss or damage to the goods is transferred from the seller to the buyer once the goods are under the carrier’s supervision.
Note that in CPT the seller is not responsible for loading the goods. According to experience, it is better to use the CPT method in land, air and combined transport (two modes of transport).
CIP: CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO Shipping and insurance fee paid to the designated place of destination
CIP is like CPT, except that the seller pays for the freight insurance to the destination.
Again, in CIP, the seller is not responsible for the loading of the goods, despite the fact that he pays the freight and insurance of the goods.
DAF: DELIVERED AT FRONTIER DELIVERY AT THE CUSTOMS BORDER
DAF means that the seller clears the goods for export and provides them to the buyer at the place specified in the contract before the customs border of the neighboring country. Mentioning the location of the border is very important because this term can be used for any border, including the border of the country of issue or even the border of the country of entry. DAF is mainly used for transportation by train and truck.
DES DUTY PAID: DELIVERED EX SHIP DELIVERY FROM SHIP
DES means that the seller places the goods at the port of destination on the ship carrying the goods before clearance for entry.
DEQ: DELIVERED EX QUAY Delivery at destination port and tolls paid with mention of destination port
In DEQ, the seller’s duty ends when the goods are delivered to the buyer at the port at the designated port of destination, after the goods have been cleared. The seller assumes all responsibilities and costs, including duties and taxes, commercial profits and customs duties at the destination.
Let the merchants know that DEQ is used under two headings: paid and unpaid tolls. Delivery at the port of destination and tolls paid means that the seller must obtain a permit to enter the goods in the destination country and arrange customs formalities at the destination in accordance with the regulations of the destination country and taxes and customs duties and remove the goods from customs and Give the green customs license to the buyer. However, in the case of DEQ, the seller pays the unpaid duties at the port of the destination country at customs, and the buyer is obliged to obtain an import permit from the destination country and pay customs formalities and customs fees.
DDU: DELIVERED DUTY UNPAID Delivery of goods to the buyer Unpaid tolls
DDU means that the seller delivers the goods to the destination and performs customs fees and formalities in addition to paying duties and taxes.
DDP: DELIVERED DUTIES PAID TO DELIVER the goods to the buyer, paid tolls
DDP means that the seller has a duty at the destination customs to pay the import duties to the country of destination and to collect duties and taxes and to accept the goods at the destination by performing customs formalities.
Incoterms DAF
Delivery of goods at the border
The term delivery of goods at the border means that the seller delivers the goods when, after clearance for export and not for entry, on the vehicle bringing the goods, unloaded at the point and place specified at the border, but Before the customs border of the neighboring country – provide to the buyer. The term border may be used for any border, including the border of the exporting country. Therefore, it is important that the desired border is always determined by mentioning the name of the point and place in the term.
Of course, if the parties want the seller to take responsibility for unloading the goods from the vehicle that brought it and bear the risks and costs of unloading, he clarifies this by adding a clear phrase in the sales contract.
The term is used for a variety of modes of transportation and when the goods are delivered at the land border.
When delivering goods at the port of destination, on board the ship or on the dock, the terms delivery on board the ship at destination DES and delivery at the dock at the port of destination DEQ must be used.
